Date: Tue, 2 Jul 2024 10:22:36 +0200
wt., 2 lip 2024 o 07:48 pifminns deettnta via Std-Proposals <
std-proposals_at_[hidden]> napisał(a):
> LOL. It is a real discussion, LOL. If WG21 knows what real discussion is,
> they won't add bs like C++ format, for example, that keeps changing its
> interface with every C++ standard. WG21 is woke. GO WOKE GO BROKE.
>
> You still do not explain how
> someheader.hpp
>
> inline void foo() noexcept
> {
> //dosomethingheader
> }
>
>
> bar.cppm
> module;
> #include<someheader.hpp>
> export module bar;
> export inline void foo() noexcept;
>
> main.cpp
> Import bar;
> #include<someheader.hpp>
> Int main()
> {
> foo(); //which foo()? The foo in the header or the foo in the
> module?
> }
>
> could work?
>
> For example, I have a class or function implementation in this
> "someheader" how does the compiler know which one to use? You literally
> breaks header only libraries.
>
>
Do you test it on the compiler or you guess? I tried to be cheratible but
now it looks
like you are criticizing your imagination of modules, not real
implementation of the standard.
As far as I know in this case both should have the same name mangling and
should not matter what was chosen.
> Some people have reported in the reddit 2 days ago. They found that
>
> import std;
> #include <vector> //or any other header does not work.
>
>
As far I know you simply need a swap order to make it work.
> Unless you fix the symbol conflict issues I mentioned, you just break
> existing code that is using headers.
>
> What I proposed is that the inline keyword should extend to classes and
> everything so that the compiler is allowed to discard definitions freely
> and keep only one copy of them, just like the inline keyword does to
> translation units. This would prevent ODR violations. Discard duplicates.
>
>
> .o file absolutely bloats, which is why glibc and many other C libraries
> are so bloated. libcs like musl literally HAVE TO put every single function
> into different translation units to avoid bloat. How is that not an issue?
>
> https://godbolt.org/z/db5snsb3K
> <https://godbolt.org/z/db5snsb3K>
> Compiler Explorer - C++ (x86-64 gcc (trunk))
> <https://godbolt.org/z/db5snsb3K>
> void foo() { } inline void bar() { } void baz() { bar(); }
> godbolt.org
> Even people use foo() function. The compiler still emits dead code of foo.
> To say it does not bloat which is laughable. Inline keyword becomes the
> meaning of "preventing compiler emits dead function" for GCC and clang in
> reality.
>
> I try this #include<iostream>
>
> #include<iostream>
>
And where are modules??? Did you even read this discussion? How much blot
has MSVC? Zero.
Please test first the thing that you are criticizing.
>
> int main()
> {
> }
>
> .file "hello.cc"
> .text
> /APP
> .globl _ZSt21ios_base_library_initv
> /NO_APP
> .section .text.startup,"x"
> .p2align 4
> .globl main
> .def main; .scl 2; .type 32; .endef
> .seh_proc main
> main:
> .LFB2258:
> subq $40, %rsp
> .seh_stackalloc 40
> .seh_endprologue
> call __main
> xorl %eax, %eax
> addq $40, %rsp
> ret
> .seh_endproc
> .def __main; .scl 2; .type 32; .endef
> .ident "GCC: (GNU) 15.0.0 20240629 (experimental)"
> The GCC compiler still emits .globl _ZSt21ios_base_library_initv
>
> g++ -o hello hello.cc -static-libstdc++ -s -flto
>
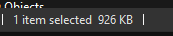
> The binary size is 926kb
>
> Without #include<iostream>
>
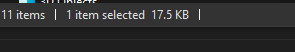
> The binary size is only 17.5kb.
>
> How is that not an issue?
>
>
>
> For the freestanding part, unlike Rust, it has a no_std one. C++ does not
> have that module. It does not have std.fundamental, as the proposal asked.
> By the way, the freestanding headers may work differently than the
> non-freestanding version unless you provide something like an inline class
> to force the discard of the same class for the ODR violations as today's
> inline does. It does not work out. Building a freestanding toolchain does
> not work out. GNU libstdc++ requires you to always provide libc for most of
> its targets even you pass --disable-hosted-libstdcxx since it does not pass
> sanity check. Libc++ completely ignores freestanding. Linux kernel drivers
> require you to use hosted x86_64-linux-gnu toolchain to build kernel
> modules. Same with windows mingw-w64 crts. Unless you fix the symbol
> conflict issues i mentioned, you just break existing code that are using
> headers.
>
>
>
>
> Do you really want to promote the unhinged rant of an abusive troll who
> attacks, harasses, and wishes death on the people trying to improve C++?
> What is his "concern"? He's added a #error to his project nobody uses so
> that if you use a compiler that supports C++20 modules you can't use his
> code. How is that reasonable?
>
>
> LOL. My library does not work when someone uses a module. Of course, I
> have to block the feature to prevent issues. If someone wants to use it,
> they HAVE to disable the module to work correctly because the C++ standard
> does not solve the problem of ODR violation here. Every compiler has a
> toggle to disable the C++ module, just like people disable exceptions and
> RTTI. What's the problem?
>
> Also why do you care a library you think nobody uses? Did I even ask you
> to use it? Why do you even care?
>
What problem make it a module? Besides, will there be multiple years before
anyone will use the `std` module and you stop people today from using new
compilers?
Where is loginc in this? Could you better ask compiler vendors to add some
tools to detect corner cases and prevent
> --
> Std-Proposals mailing list
> Std-Proposals_at_[hidden]
> https://lists.isocpp.org/mailman/listinfo.cgi/std-proposals
>
std-proposals_at_[hidden]> napisał(a):
> LOL. It is a real discussion, LOL. If WG21 knows what real discussion is,
> they won't add bs like C++ format, for example, that keeps changing its
> interface with every C++ standard. WG21 is woke. GO WOKE GO BROKE.
>
> You still do not explain how
> someheader.hpp
>
> inline void foo() noexcept
> {
> //dosomethingheader
> }
>
>
> bar.cppm
> module;
> #include<someheader.hpp>
> export module bar;
> export inline void foo() noexcept;
>
> main.cpp
> Import bar;
> #include<someheader.hpp>
> Int main()
> {
> foo(); //which foo()? The foo in the header or the foo in the
> module?
> }
>
> could work?
>
> For example, I have a class or function implementation in this
> "someheader" how does the compiler know which one to use? You literally
> breaks header only libraries.
>
>
Do you test it on the compiler or you guess? I tried to be cheratible but
now it looks
like you are criticizing your imagination of modules, not real
implementation of the standard.
As far as I know in this case both should have the same name mangling and
should not matter what was chosen.
> Some people have reported in the reddit 2 days ago. They found that
>
> import std;
> #include <vector> //or any other header does not work.
>
>
As far I know you simply need a swap order to make it work.
> Unless you fix the symbol conflict issues I mentioned, you just break
> existing code that is using headers.
>
> What I proposed is that the inline keyword should extend to classes and
> everything so that the compiler is allowed to discard definitions freely
> and keep only one copy of them, just like the inline keyword does to
> translation units. This would prevent ODR violations. Discard duplicates.
>
>
> .o file absolutely bloats, which is why glibc and many other C libraries
> are so bloated. libcs like musl literally HAVE TO put every single function
> into different translation units to avoid bloat. How is that not an issue?
>
> https://godbolt.org/z/db5snsb3K
> <https://godbolt.org/z/db5snsb3K>
> Compiler Explorer - C++ (x86-64 gcc (trunk))
> <https://godbolt.org/z/db5snsb3K>
> void foo() { } inline void bar() { } void baz() { bar(); }
> godbolt.org
> Even people use foo() function. The compiler still emits dead code of foo.
> To say it does not bloat which is laughable. Inline keyword becomes the
> meaning of "preventing compiler emits dead function" for GCC and clang in
> reality.
>
> I try this #include<iostream>
>
> #include<iostream>
>
And where are modules??? Did you even read this discussion? How much blot
has MSVC? Zero.
Please test first the thing that you are criticizing.
>
> int main()
> {
> }
>
> .file "hello.cc"
> .text
> /APP
> .globl _ZSt21ios_base_library_initv
> /NO_APP
> .section .text.startup,"x"
> .p2align 4
> .globl main
> .def main; .scl 2; .type 32; .endef
> .seh_proc main
> main:
> .LFB2258:
> subq $40, %rsp
> .seh_stackalloc 40
> .seh_endprologue
> call __main
> xorl %eax, %eax
> addq $40, %rsp
> ret
> .seh_endproc
> .def __main; .scl 2; .type 32; .endef
> .ident "GCC: (GNU) 15.0.0 20240629 (experimental)"
> The GCC compiler still emits .globl _ZSt21ios_base_library_initv
>
> g++ -o hello hello.cc -static-libstdc++ -s -flto
>
> The binary size is 926kb
>
> Without #include<iostream>
>
> The binary size is only 17.5kb.
>
> How is that not an issue?
>
>
>
> For the freestanding part, unlike Rust, it has a no_std one. C++ does not
> have that module. It does not have std.fundamental, as the proposal asked.
> By the way, the freestanding headers may work differently than the
> non-freestanding version unless you provide something like an inline class
> to force the discard of the same class for the ODR violations as today's
> inline does. It does not work out. Building a freestanding toolchain does
> not work out. GNU libstdc++ requires you to always provide libc for most of
> its targets even you pass --disable-hosted-libstdcxx since it does not pass
> sanity check. Libc++ completely ignores freestanding. Linux kernel drivers
> require you to use hosted x86_64-linux-gnu toolchain to build kernel
> modules. Same with windows mingw-w64 crts. Unless you fix the symbol
> conflict issues i mentioned, you just break existing code that are using
> headers.
>
>
>
>
> Do you really want to promote the unhinged rant of an abusive troll who
> attacks, harasses, and wishes death on the people trying to improve C++?
> What is his "concern"? He's added a #error to his project nobody uses so
> that if you use a compiler that supports C++20 modules you can't use his
> code. How is that reasonable?
>
>
> LOL. My library does not work when someone uses a module. Of course, I
> have to block the feature to prevent issues. If someone wants to use it,
> they HAVE to disable the module to work correctly because the C++ standard
> does not solve the problem of ODR violation here. Every compiler has a
> toggle to disable the C++ module, just like people disable exceptions and
> RTTI. What's the problem?
>
> Also why do you care a library you think nobody uses? Did I even ask you
> to use it? Why do you even care?
>
What problem make it a module? Besides, will there be multiple years before
anyone will use the `std` module and you stop people today from using new
compilers?
Where is loginc in this? Could you better ask compiler vendors to add some
tools to detect corner cases and prevent
> --
> Std-Proposals mailing list
> Std-Proposals_at_[hidden]
> https://lists.isocpp.org/mailman/listinfo.cgi/std-proposals
>
Received on 2024-07-02 08:22:48